146. LRU缓存机制
题目
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制。它应该支持以下操作: 获取数据 get 和 写入数据 put 。
获取数据 get(key) - 如果关键字 (key) 存在于缓存中,则获取关键字的值(总是正数),否则返回 -1。
写入数据 put(key, value) - 如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字/值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
进阶:
你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
示例:
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 /* 缓存容量 */ );
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1); // 返回 1
cache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废
cache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废
cache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.get(3); // 返回 3
cache.get(4); // 返回 4
方法
题目要求我们构建一个数据结构,并实现两种API:put操作和get操作,因为要在O(1)时间复杂度内完成这两种操作,所以这一数据结构要求满足以下几个特点:插入快、查找快、删除快、并且有序(因为需要有序来区分最近使用的和久未使用的数据)。
考虑我们学过的数据结构,链表可以做到有序,插入和删除也快,但是查找操作很慢。哈希表的插入查找删除都为O(1),但是不能做到有序。因此将两个结构相结合,构成哈希链表,即可同时拥有以上特性。
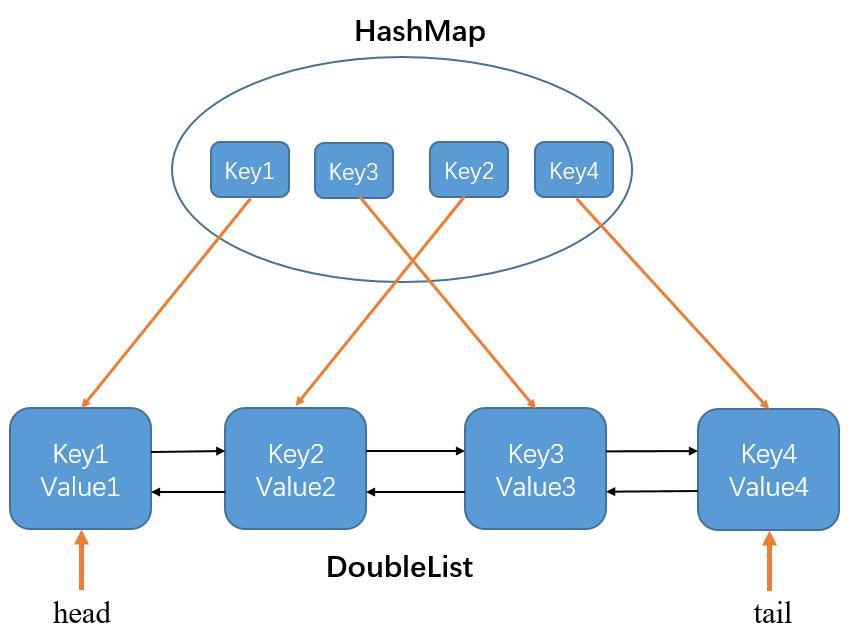
因此,我们需要同时维护一个哈希表和一个双向链表,双向链表的节点中存放数据结构Node(包括key和value),哈希表的键为key,值为存放这个key的Node节点。如下图所示:
Node类如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| class Node{
private int key, value;
private Node next, pre;
public Node(int k, int v){
this.key = k;
this.value = v;
}
}
|
双向链表DoubleList类如下(包括4个时间复杂度均为O(1)的实例方法):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| class DoubleList{
private Node head, tail;
private int size;
public void addFirst(Node x){
if(head == null)
head = tail = x;
else {
x.next = head;
head.pre = x;
head = x;
}
size++;
}
public void remove(Node x){
if(x == head && x == tail){
head = null;
tail = null;
}
else if(x == tail){
x.pre.next = null;
tail = x.pre;
}
else if(x == head){
x.next.pre = null;
head = x.next;
}
else {
x.pre.next = x.next;
x.next.pre = x.pre;
}
size--;
}
public Node removeLast(){
Node node = tail;
remove(tail);
return node;
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
}
|
有了以上两个结构,我们在LRU算法中将哈希表和双向链表结合起来即可,就可以在实现LRU算法的同时,将get和put这两操作的时间复杂度控制在O(1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| class LRUCache {
private HashMap<Integer, Node> map;
private DoubleList cache;
private int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity){
this.capacity = capacity;
map = new HashMap<>();
cache = new DoubleList();
}
public int get(int key){
if(!map.containsKey(key))
return -1;
int value = map.get(key).value;
put(key, value);
return value;
}
public void put(int key, int value){
Node x = new Node(key, value);
if(map.containsKey(key)){
cache.remove(map.get(key));
cache.addFirst(x);
map.put(key, x);
}
else{
if(capacity == cache.size()){
Node last = cache.removeLast();
map.remove(last.key);
}
cache.addFirst(x);
map.put(key, x);
}
}
}
|
